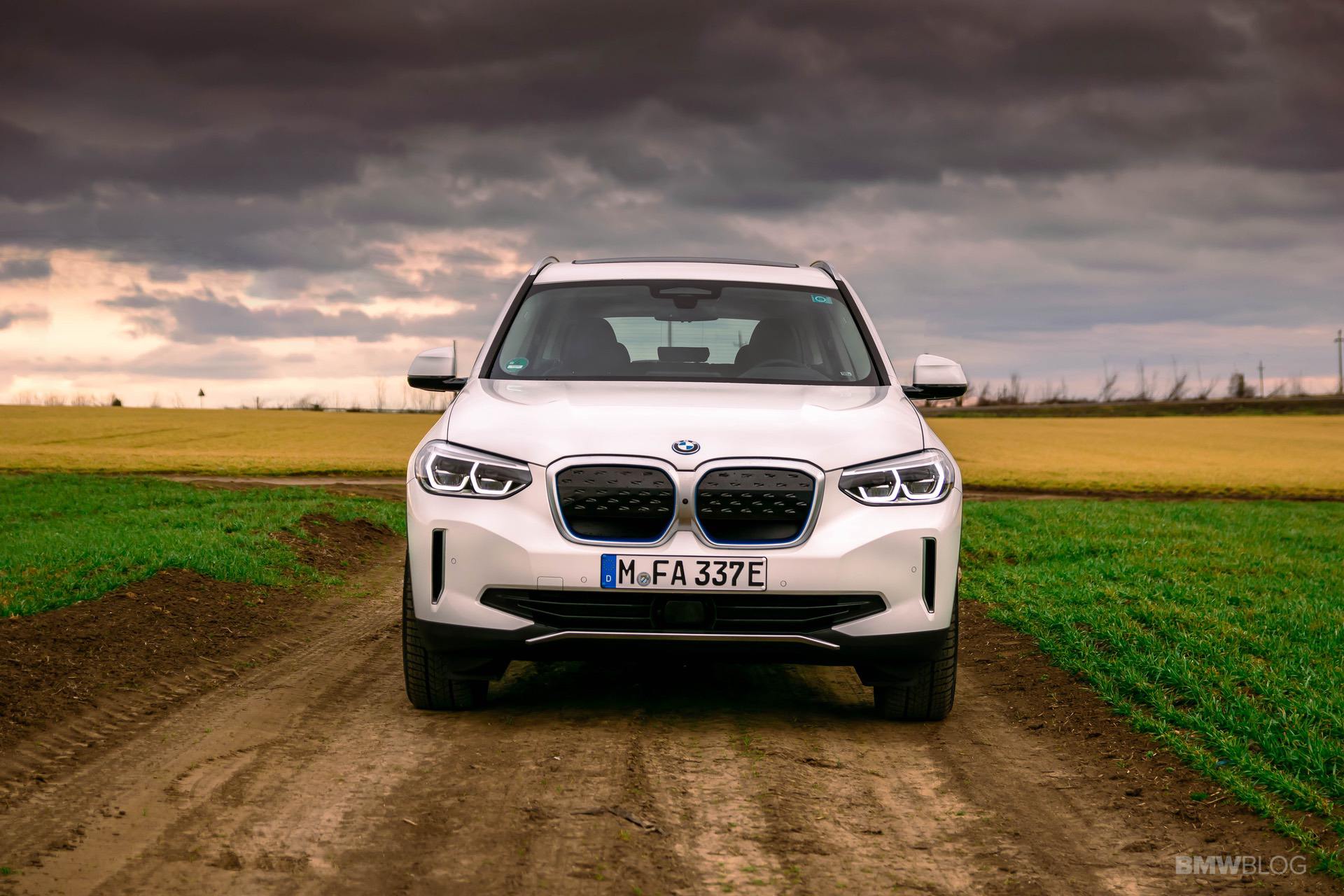
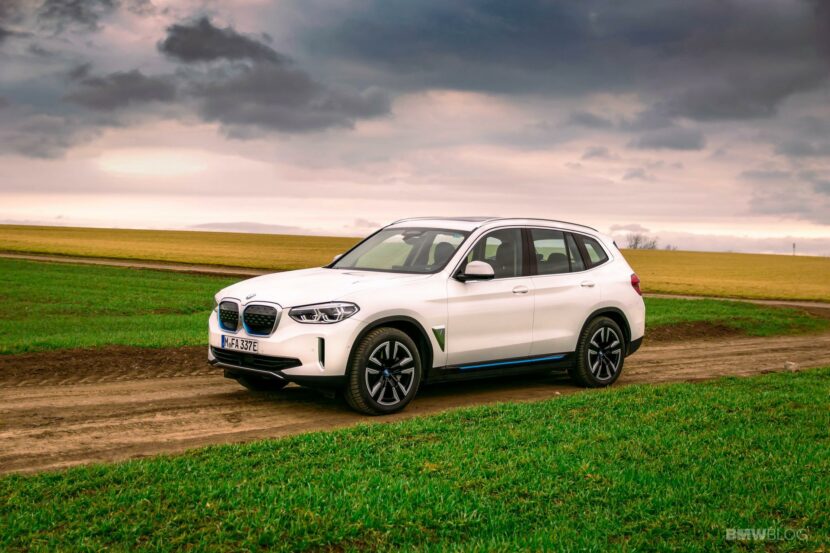
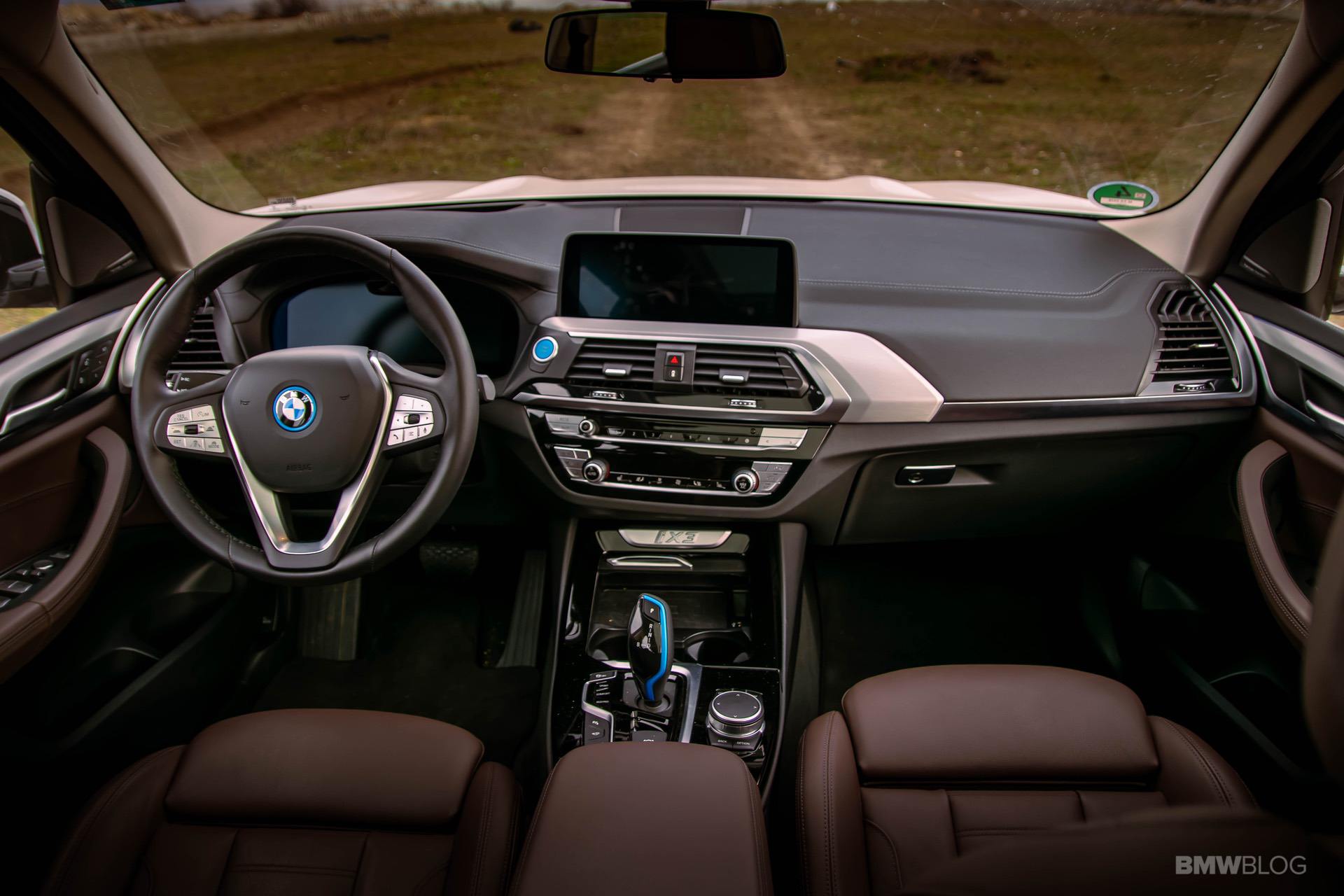
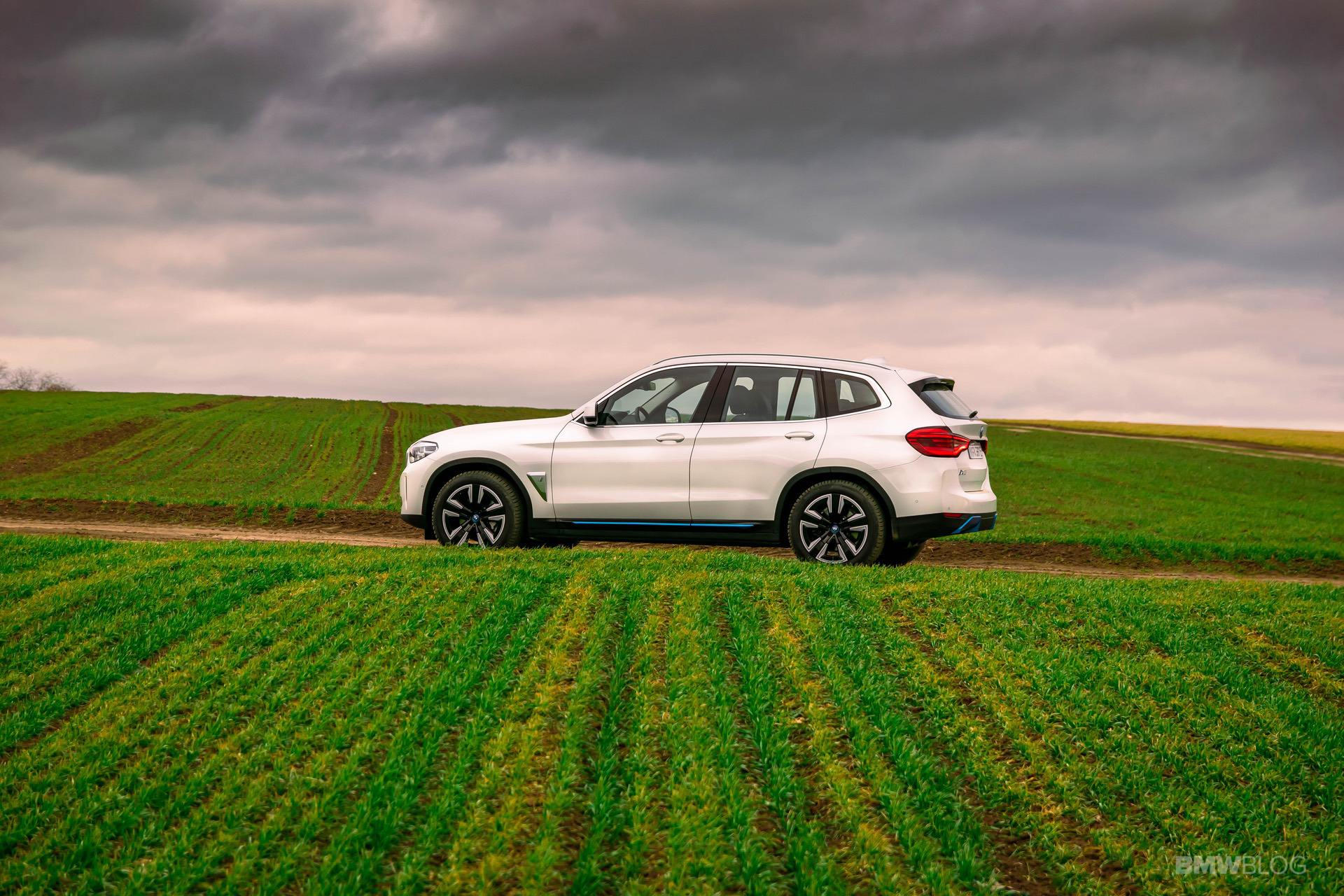
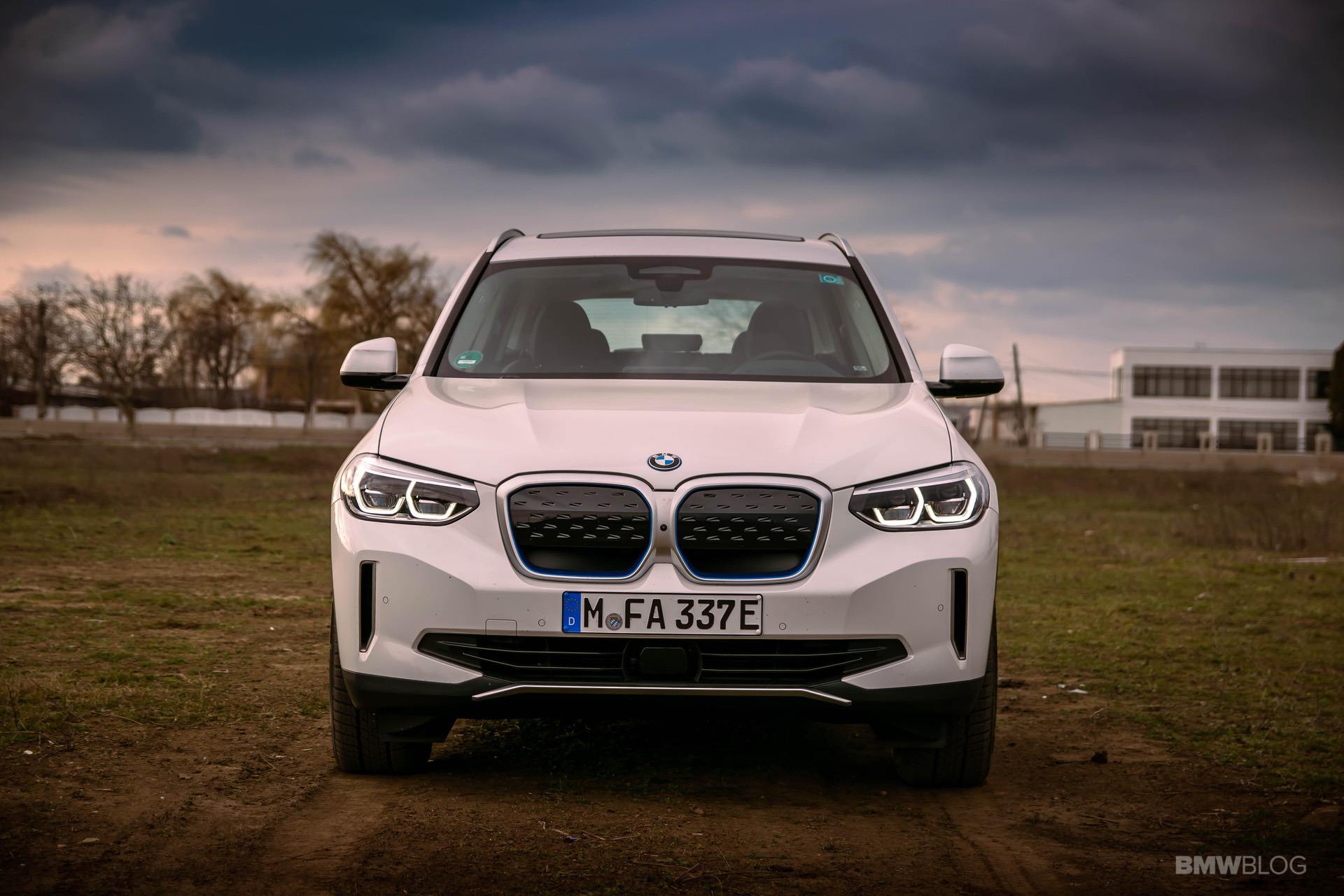
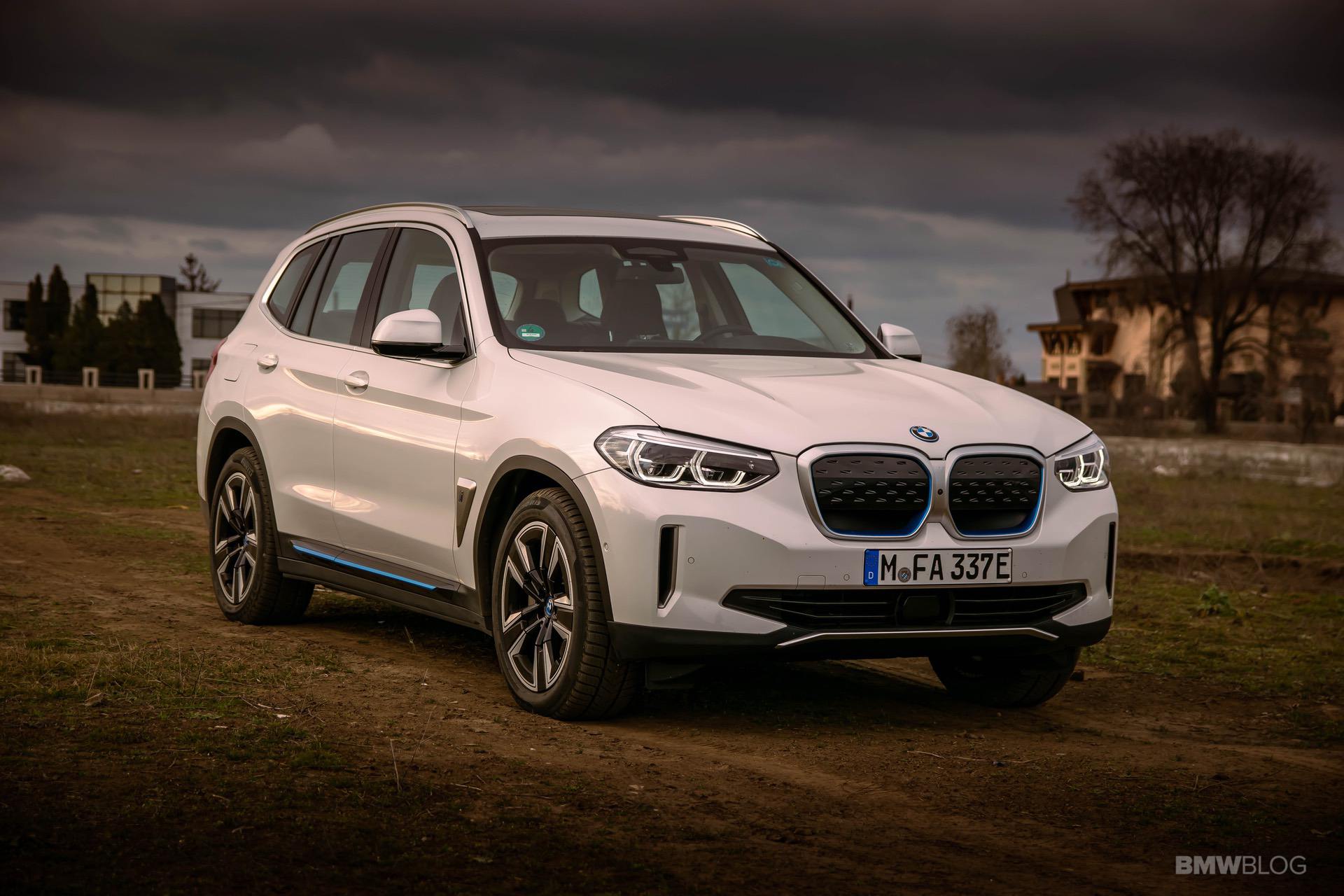
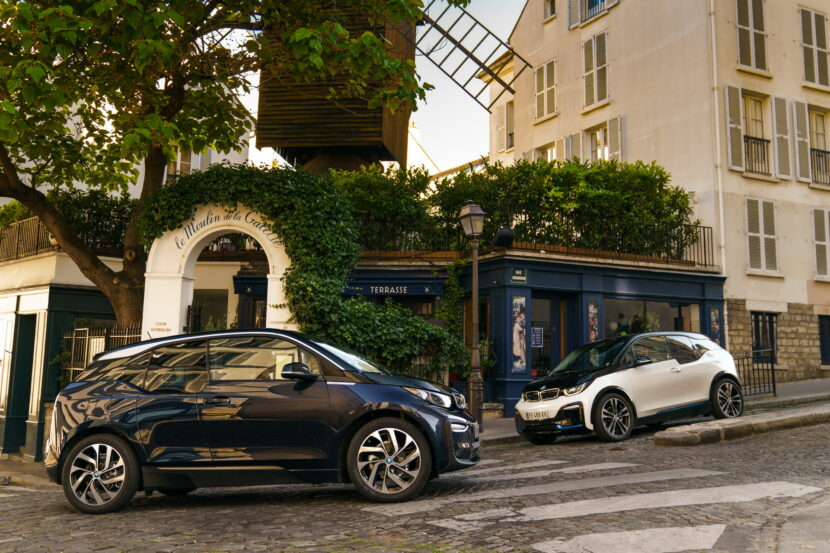The world is changing at a faster pace than ever. Most of the credit goes to the rapid tech advancements in all fields. At the same time, this change doesn’t seem to happen fast enough in some industries. The automotive world is one of them. Even though there were some pioneers, including the BMW Group. In 2011, the Bavarians founded the BMW i division, and this was supposed to be the specialist arm of the Bavarians, focused solely on electric drivetrains and alternatives to internal combustion engines.
BMW i – Born In 2011
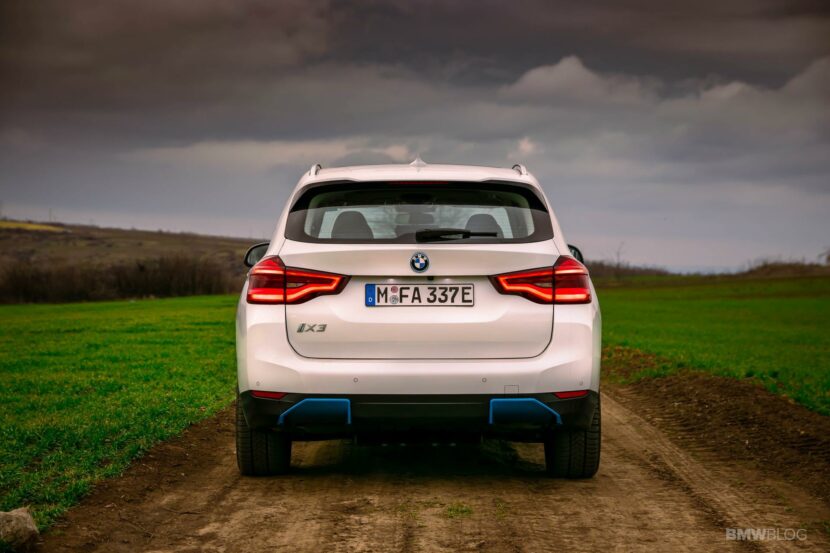
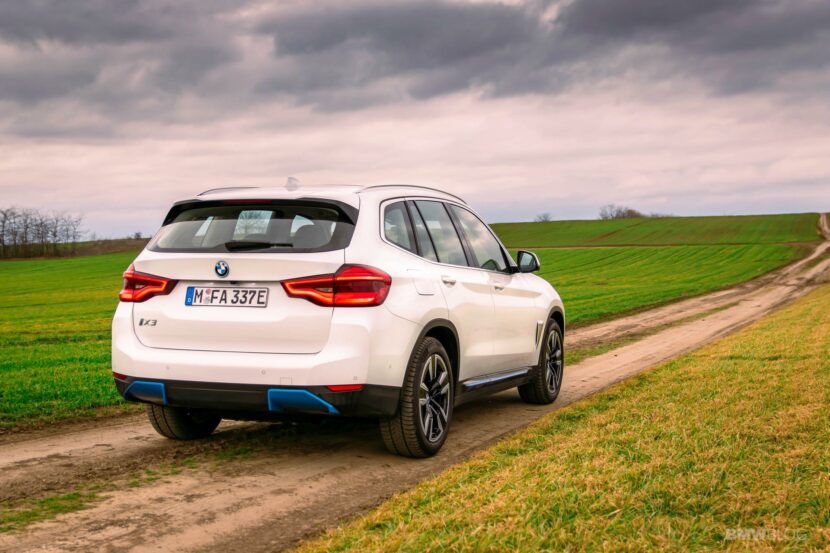
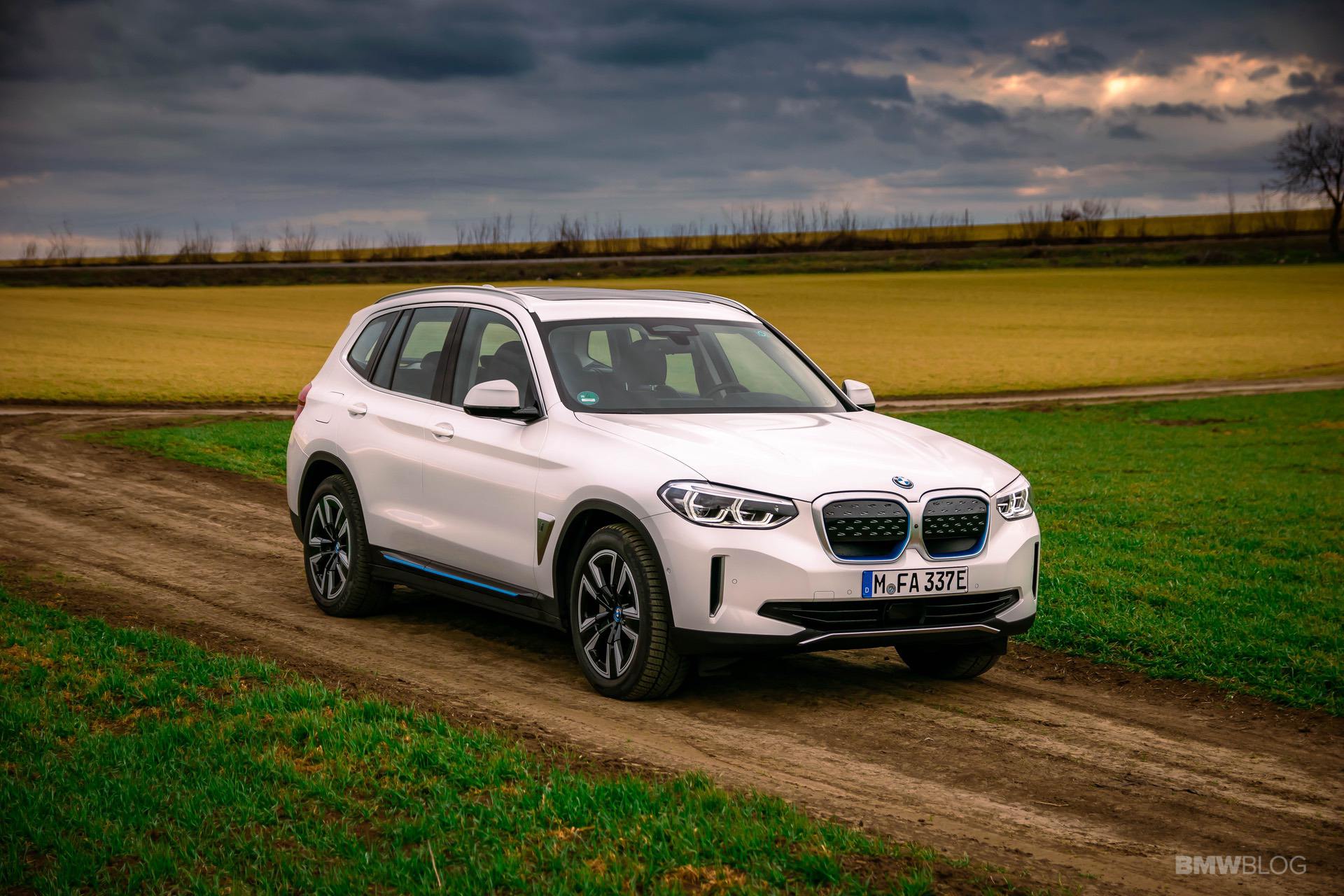
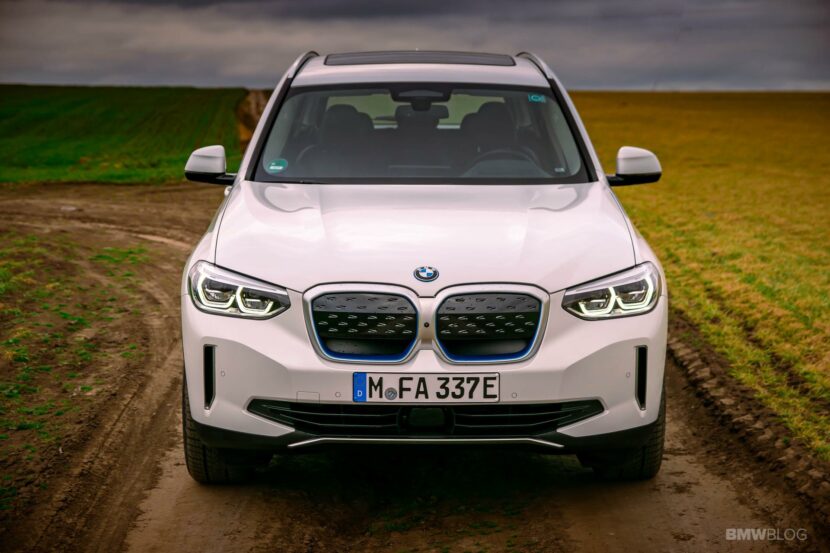
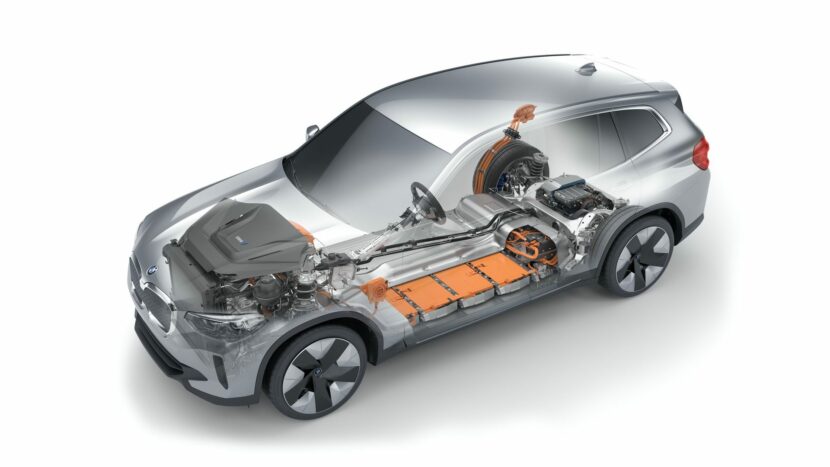
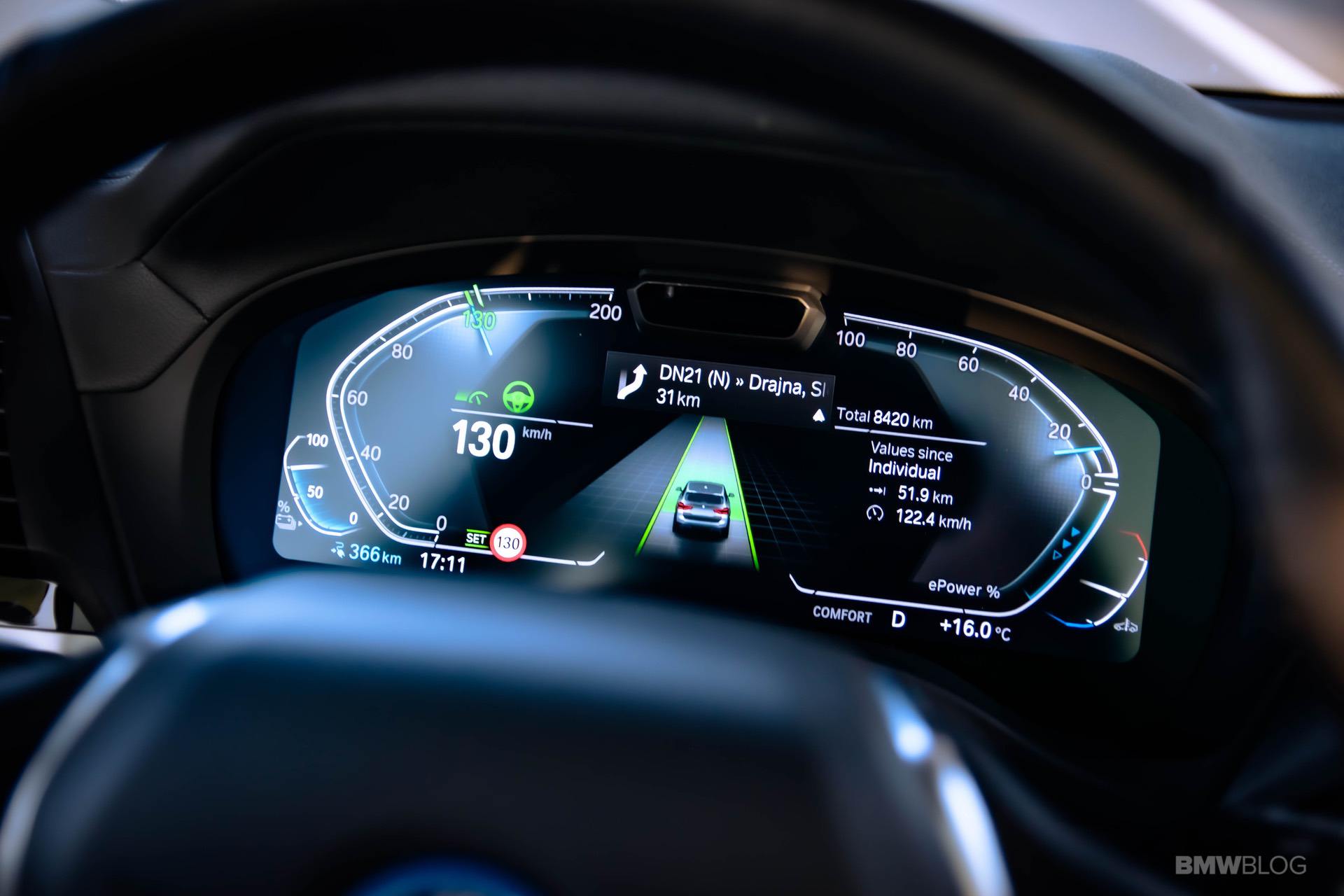
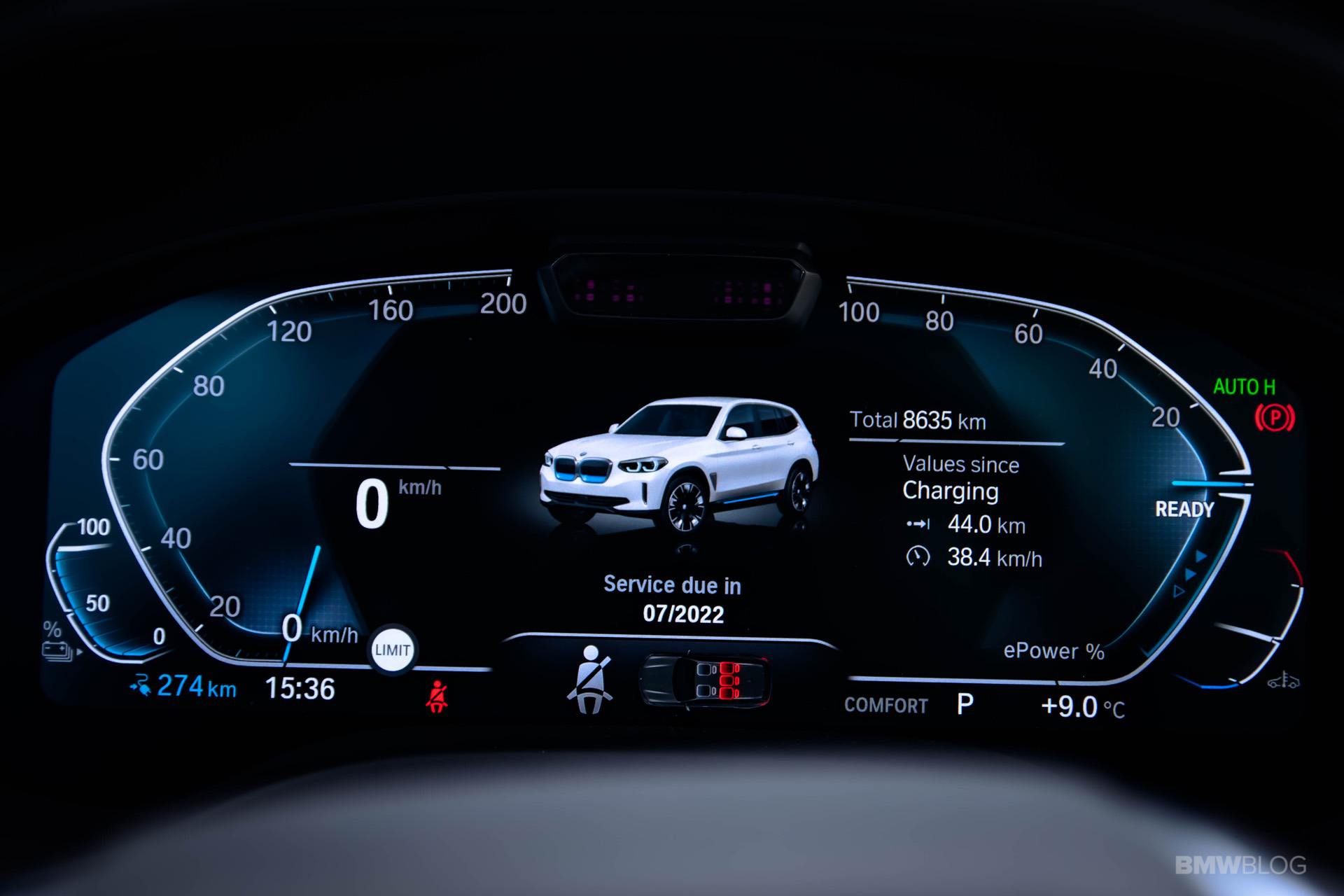
The BMW i engineers started cranking out new technologies at a fast pace. One clear example in this regard is the BMW i3, their flagship EV, if you will. Even eight years later, the i3 is still the only car you can buy under $100,000 with a carbon fiber monocoque layout. But the more important thing to remember about the i3 is that it now has its third different battery pack to rely on. And over the course of just about 6 years, its energy storage capacity more than doubled. All that was done without physically increasing the size of the huge battery pack in the floor.
And that seems to be the key to a truly electric future, a future that is so uncertain, most companies don’t really know what the perfect recipe to tackle it is.
At the moment, there are two different philosophies at play in the automotive industry. On the one hand, we have companies with dedicated EV platforms which allows them to build electric cars from the ground up with no limitations. These platforms would be adjustable and allow you to make the most out of the specifics of an electric car. From adjusting the design, to offering more space inside than a similarly sized internal combustion engine car. The problem with this approach is that it’s costly and you’re investing a lot in a platform that may not cater to all the needs your customers have.
Other car makers opted for a modular platform that can house both purely electric cars and internal combustion engine. That means they can build both types of cars on the same assembly line, with the same overall chassis design, allowing you to be very flexible and adapt to the customer demand. This is what BMW is doing and they call it ‘The Power of Choice’.
It’s a risky strategy that does come with a couple of shortcomings. For example, a car that was designed to use an internal combustion engine will have some issues with interior space, with weight distribution and even practicality once is converted to an EV. But that can be overlooked if the car in question is good enough for the customer.